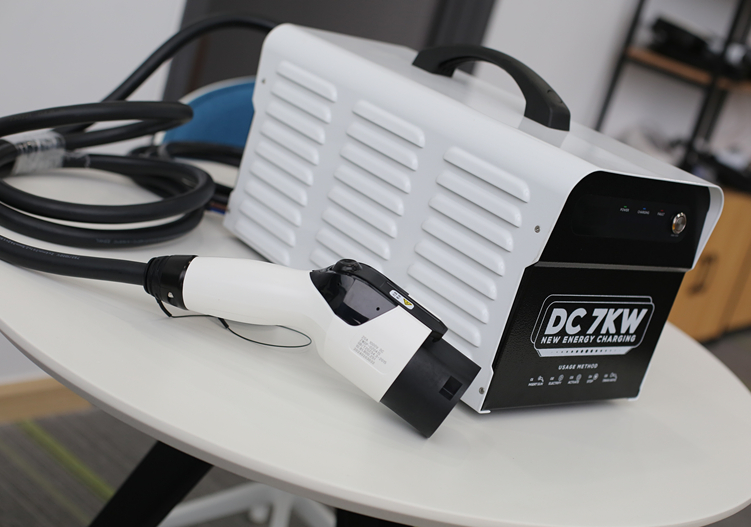
What are the main differences between AC charging and DC CHARGING?
AC (Alternating Current) charging and DC (Direct Current) charging are two different methods of delivering electrical energy to electric vehicles (EVs). Here are the main differences between AC charging and DC charging:
1. Type of Current:
· AC Charging: Alternating Current is used. This is the type of electricity commonly used in homes and businesses.
· DC Charging: Direct Current is used. This is the type of electricity typically stored in batteries and used in many electronic devices.
2. Voltage:
· AC Charging: Lower voltage, typically ranging from 110V to 240V in residential settings and up to 400V in commercial settings.
· DC Charging: Higher voltage, usually above 400V, enabling faster charging.
3. Charging Speed:
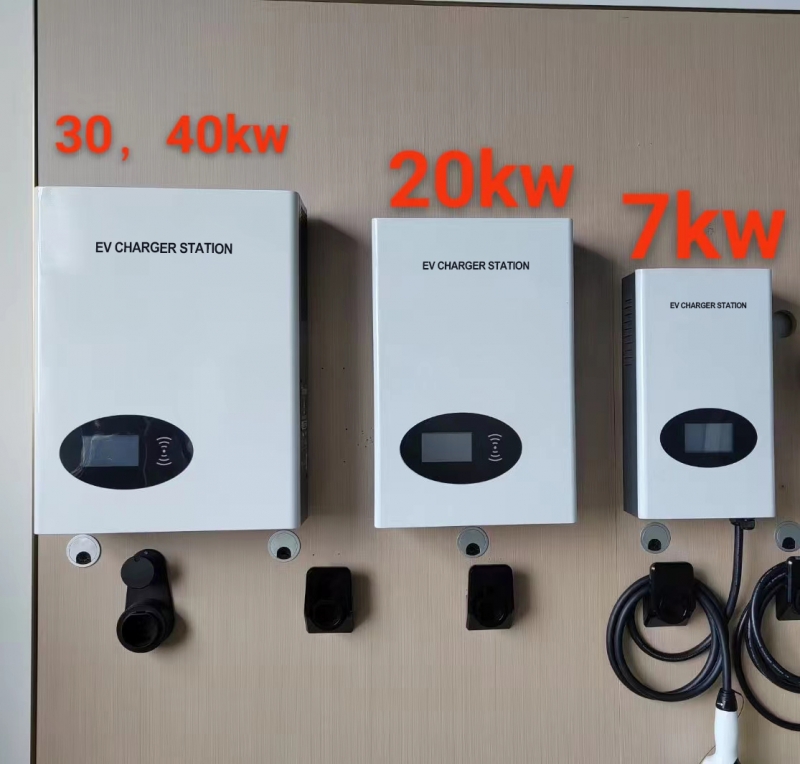
· AC Charging: Slower charging compared to DC. AC charging stations are suitable for overnight charging at home or for longer stays at destinations.
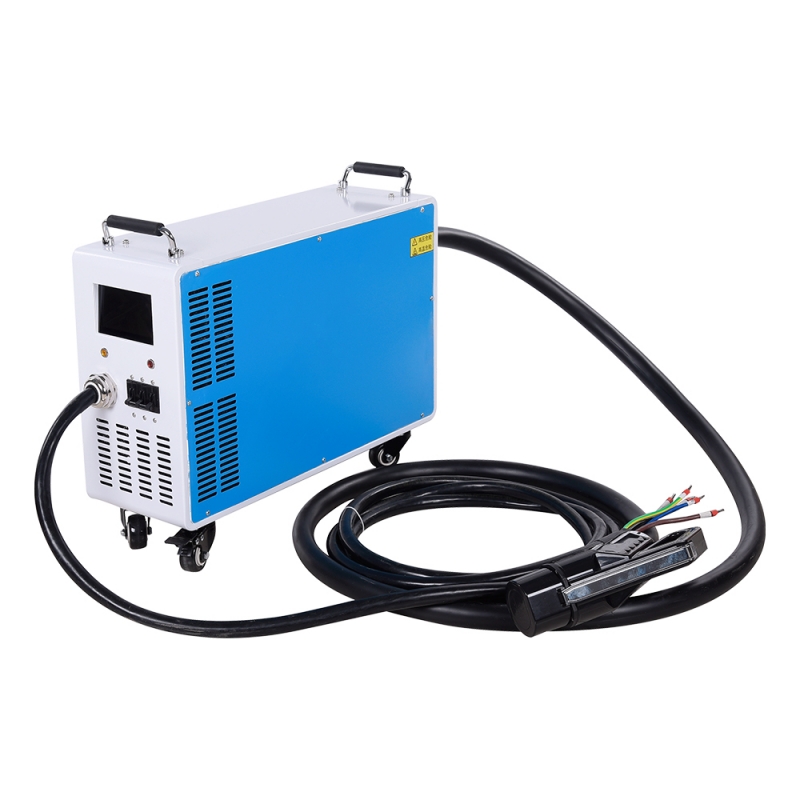
· DC Charging: Faster charging. DC fast chargers can provide a significant amount of energy to the battery in a relatively short time, making them suitable for quick charging during travel.
4. Converter Requirement:
· AC Charging: EVs have an onboard charger that converts AC power to DC power to charge the battery.
· DC Charging: The electricity is supplied directly to the vehicle's battery without the need for an onboard converter, which makes DC charging more efficient.
5. Station Cost and Complexity:
· AC Charging: Generally, AC charging stations are less expensive to install and maintain. They are common in residential areas and workplaces.
· DC Charging: DC fast charging stations are more complex and expensive to install. They are often found along highways and at locations where quick charging is essential.
6. Use Cases:
· AC Charging: Suited for daily charging routines, where longer charging times are acceptable.
· DC Charging: Suited for long-distance travel and situations where a quick charge is needed.
7. Compatibility:
· AC Charging: Nearly all electric vehicles come with onboard AC chargers, making them compatible with AC charging stations.
· DC Charging: Some electric vehicles are equipped with DC fast-charging capabilities. Not all EVs support DC fast charging, so compatibility varies.
In summary, AC charging is more suitable for routine charging at home or work, while DC charging is designed for fast charging, particularly during travel to enable longer trips without extended charging stops. Many EVs have the ability to use both AC and DC charging, providing flexibility for different charging scenarios.
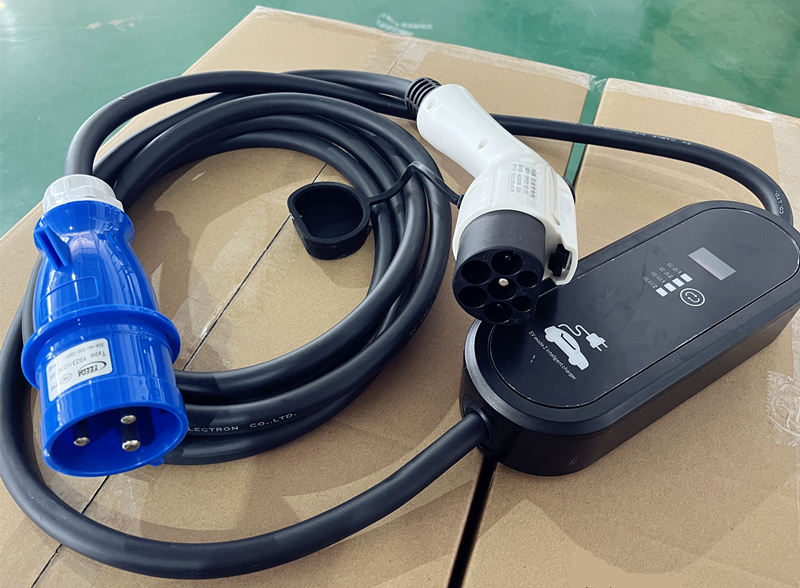
3, how to choose a correct EVSE for your car?
Choosing the right portable charger for your electric vehicle (EV) involves considering several factors to ensure compatibility, efficiency, and convenience. Here are the main factors to consider:
Shenzhen Sympres Technology Co. Ltd
a leading supplier of innovative and reliable EV chargers and wallbox chargers
www.symplug.com
Whatsapp: +8613537523979







 Send Email
Send Email Jane_ev
Jane_ev